Custom Web Server
Modern.js encapsulates most server-side capabilities required by projects, typically eliminating the need for server-side development. However, in certain scenarios such as user authentication, request preprocessing, or adding page skeletons, custom server-side logic may still be necessary.
Starting a Custom Web Server
You must ensure that the Modern.js version is x.67.5 or above.
Developers can execute the pnpm run new command in the project root directory to start the "Custom Web Server" feature:
? Select operation: Create project element
? Select element type: Create "Custom Web Server" source directoryAfter executing the command, a server/modern.server.ts file will be automatically created in the project directory, where you can write custom logic.
Capabilities of the Custom Web Server
Modern.js's Web Server is based on Hono, and in the latest version of the Custom Web Server, we expose Hono's middleware capabilities, you can refer to Hono API for more usage.
In the server/modern.server.ts file, you can add the following configurations to extend the Server:
- Middleware
- Render Middleware
- Server-side Plugin
In the Plugin, you can define Middleware and RenderMiddleware. The middleware loading process is illustrated in the following diagram:
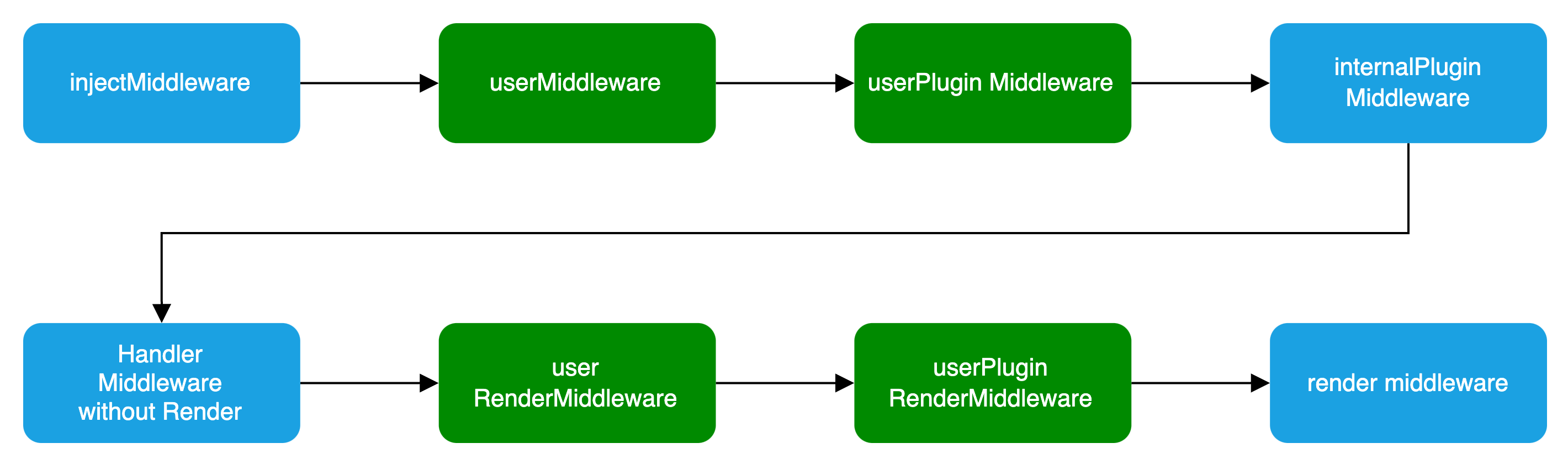
Basic Configuration
import { defineServerConfig } from '@modern-js/server-runtime';
export default defineServerConfig({
middlewares: [],
renderMiddlewares: [],
plugins: [],
onError: () => {},
});Type Definition
defineServerConfig type definition is as follows:
import type { MiddlewareHandler } from 'hono';
type MiddlewareOrder = 'pre' | 'post' | 'default';
type MiddlewareObj = {
name: string;
path?: string;
method?: 'options' | 'get' | 'post' | 'put' | 'delete' | 'patch' | 'all';
handler: MiddlewareHandler | MiddlewareHandler[];
before?: Array<MiddlewareObj['name']>;
order?: MiddlewareOrder;
};
type ServerConfig = {
middlewares?: MiddlewareObj[];
renderMiddlewares?: MiddlewareObj[];
plugins?: ServerPlugin[];
onError?: (err: Error, c: Context) => Promise<any> | any;
};Middleware
Middleware supports executing custom logic before and after the request handling and page routing processes in Modern.js services. If custom logic needs to handle both API routes and page routes, Middleware is the clear choice.
If you only need to handle BFF API routes, you can determine whether a request is for a BFF API by checking if req.path starts with the BFF prefix.
Usage is as follows:
import {
defineServerConfig,
type MiddlewareHandler,
} from '@modern-js/server-runtime';
export const handler: MiddlewareHandler = async (c, next) => {
const monitors = c.get('monitors');
const start = Date.now();
await next();
const end = Date.now();
// Report Duration
monitors.timing('request_timing', end - start);
};
export default defineServerConfig({
middlewares: [
{
name: 'request-timing',
handler,
},
],
});
You must execute the next function to proceed with the subsequent Middleware.
RenderMiddleware
If you only need to handle the logic before and after page rendering, modern.js also provides rendering middleware, which can be used as follows:
import {
defineServerConfig,
type MiddlewareHandler,
} from '@modern-js/server-runtime';
// Inject render performance metrics
const renderTiming: MiddlewareHandler = async (c, next) => {
const start = Date.now();
await next();
const end = Date.now();
c.res.headers.set('server-timing', `render; dur=${end - start}`);
};
// Modify the Response Body
const modifyResBody: MiddlewareHandler = async (c, next) => {
await next();
const { res } = c;
const text = await res.text();
const newText = text.replace('<body>', '<body> <h3>bytedance</h3>');
c.res = c.body(newText, {
status: res.status,
headers: res.headers,
});
};
export default defineServerConfig({
renderMiddlewares: [
{
name: 'render-timing',
handler: renderTiming,
},
{
name: 'modify-res-body',
handler: modifyResBody,
},
],
});Plugin
Modern.js supports adding the aforementioned middleware and rendering middleware for the Server in custom plugins, which can be used as follows:
import type { ServerPlugin } from '@modern-js/server-runtime';
export default (): ServerPlugin => ({
name: 'serverPlugin',
setup(api) {
api.onPrepare(() => {
const { middlewares, renderMiddlewares } = api.getServerContext();
// Inject server-side data for page dataLoader consumption
middlewares?.push({
name: 'server-plugin-middleware',
handler: async (c, next) => {
c.set('message', 'hi modern.js');
await next();
// ...
},
});
// redirect
renderMiddlewares?.push({
name: 'server-plugin-render-middleware',
handler: async (c, next) => {
const user = getUser(c.req);
if (!user) {
return c.redirect('/login');
}
await next();
},
});
});
},
});import { defineServerConfig } from '@modern-js/server-runtime';
import serverPlugin from './plugins/serverPlugin';
export default defineServerConfig({
plugins: [serverPlugin()],
});import { useHonoContext } from '@modern-js/server-runtime';
import { defer } from '@modern-js/runtime/router';
export default () => {
const ctx = useHonoContext();
// SSR scenario consumes data injected by the Server Side
const message = ctx.get('message');
// ...
};onError
onError is a global error handling function used to capture and handle all uncaught errors in the Modern.js server. By customizing the onError function, developers can uniformly handle different types of errors, return custom error responses, and implement features such as error logging and error classification.
Below is a basic example of an onError configuration:
import { defineServerConfig } from '@modern-js/server-runtime';
export default defineServerConfig({
onError: (err, c) => {
// Log the error
console.error('Server error:', err);
// Return different responses based on the error type
if (err instanceof SyntaxError) {
return c.json({ error: 'Invalid JSON' }, 400);
}
// Customize BFF error response based on request path
if (c.req.path.includes('/api')) {
return c.json({ message: 'API error occurred' }, 500);
}
return c.text('Internal Server Error', 500);
},
});Legacy API (Deprecated)
The legacy API no longer compatible. For extending server capabilities, please refer to Custom Web Server. For migration guidelines, see Migrating to the New Version of Custom Web Server.
Unstable Middleware
Modern.js supports adding rendering middleware to the Web Server, allowing custom logic execution before and after processing page routes.
import {
UnstableMiddleware,
UnstableMiddlewareContext,
} from '@modern-js/runtime/server';
const time: UnstableMiddleware = async (c: UnstableMiddlewareContext, next) => {
const start = Date.now();
await next();
const end = Date.now();
console.log(`dur=${end - start}`);
};
export const unstableMiddleware: UnstableMiddleware[] = [time];Hooks
We recommend using UnstableMiddleware instead of Hooks.
Modern.js provides Hooks to control specific logic in the Web Server. All page requests will pass through Hooks.
Currently, two types of Hooks are available: AfterMatch and AfterRender. Developers can implement them in server/index.ts as follows:
import type {
AfterMatchHook,
AfterRenderHook,
} from '@modern-js/server-runtime';
export const afterMatch: AfterMatchHook = (ctx, next) => {
next();
};
export const afterRender: AfterRenderHook = (ctx, next) => {
next();
};Best practices when using Hooks:
- Perform authorization checks in afterMatch.
- Handle Rewrite and Redirect in afterMatch.
- Inject HTML content in afterRender.
Migrate to the New Version of Custom Web Server
Migration Background
Modern.js Server is continuously evolving to provide more powerful features. We have optimized the definition and usage of middleware and Server plugins. While the old custom Web Server approach is still compatible, we strongly recommend migrating according to this guide to fully leverage the advantages of the new version.
Migration Steps
- Upgrade Modern.js version to x.67.5 or above.
- Configure middleware or plugins in
server/modern.server.tsaccording to the new definition method. - Migrate the custom logic in
server/index.tsto middleware or plugins, and update your code with reference to the differences betweenContextandNext.
Context Differences
In the new version, the middleware handler type is Hono's MiddlewareHandler, meaning the Context type is Hono Context. The differences from the old custom Web Server's Context are as follows:
UnstableMiddleware
type Body = ReadableStream | ArrayBuffer | string | null;
type UnstableMiddlewareContext<
V extends Record<string, unknown> = Record<string, unknown>,
> = {
request: Request;
response: Response;
get: Get<V>;
set: Set<V>;
// Current Matched Routing Information
route: string;
header: (name: string, value: string, options?: { append?: boolean }) => void;
status: (code: number) => void;
redirect: (location: string, status?: number) => Response;
body: (data: Body, init?: ResponseInit) => Response;
html: (
data: string | Promise<string>,
init?: ResponseInit,
) => Response | Promise<Response>;
};Differences between UnstableMiddleware Context and Hono Context:
| UnstableMiddleware | Hono | Description |
|---|---|---|
c.request | c.req.raw | Refer to HonoRequest raw documentation |
c.response | c.res | Refer to Hono Context res documentation |
c.route | c.get('route') | Get application context information. |
loaderContext.get | honoContext.get | After injecting data using c.set, consume in dataLoader: the old version uses loaderContext.get, refer to the new version in Plugin example |
Middleware
type MiddlewareContext = {
response: {
set: (key: string, value: string) => void;
status: (code: number) => void;
getStatus: () => number;
cookies: {
set: (key: string, value: string, options?: any) => void;
clear: () => void;
};
raw: (
body: string,
{ status, headers }: { status: number; headers: Record<string, any> },
) => void;
locals: Record<string, any>;
};
request: {
url: string;
host: string;
pathname: string;
query: Record<string, any>;
cookie: string;
cookies: {
get: (key: string) => string;
};
headers: IncomingHttpHeaders;
};
source: {
req: IncomingMessage;
res: ServerResponse;
};
};Differences between Middleware Context and Hono Context:
| UnstableMiddleware | Hono | Description |
|---|---|---|
c.request.cookie | getCookie() | Refer to Hono Cookie Helper documentation |
c.request.pathname | c.req.path | Refer to HonoRequest path documentation |
c.request.url | - | Hono c.req.url provides the full request URL, calculate manually from URL |
c.request.host | c.req.header('Host') | Obtain host through header |
c.request.query | c.req.query() | Refer to HonoRequest query documentation |
c.request.headers | c.req.header() | Refer to HonoRequest header documentation |
c.response.set | c.res.headers.set | Example: c.res.headers.set('custom-header', '1') |
c.response.status | c.status | Example: c.status(201) |
c.response.cookies | c.header | Example: c.header('Set-Cookie', 'user_id=123') |
c.response.raw | c.res | Refer to Hono Context res documentation |
Hook
type HookContext = {
response: {
set: (key: string, value: string) => void;
status: (code: number) => void;
getStatus: () => number;
cookies: {
set: (key: string, value: string, options?: any) => void;
clear: () => void;
};
raw: (
body: string,
{ status, headers }: { status: number; headers: Record<string, any> },
) => void;
};
request: {
url: string;
host: string;
pathname: string;
query: Record<string, any>;
cookie: string;
cookies: {
get: (key: string) => string;
};
headers: IncomingHttpHeaders;
};
};
type AfterMatchContext = HookContext & {
router: {
redirect: (url: string, status: number) => void;
rewrite: (entry: string) => void;
};
};
type AfterRenderContext = {
template: {
get: () => string;
set: (html: string) => void;
prependHead: (fragment: string) => void;
appendHead: (fragment: string) => void;
prependBody: (fragment: string) => void;
appendBody: (fragment: string) => void;
};
};Hook Context is mostly consistent with Middleware Context, so we need to pay extra attention to the additional parts of different Hooks.
| UnstableMiddleware | Hono | Description |
|---|---|---|
router.redirect | c.redirect | Refer to Hono Context redirect documentation |
router.rewrite | - | No corresponding capability provided at the moment |
| template API | c.res | Refer to Hono Context res documentation |
Differences in Next API
In Middleware and Hooks, the render function executes even without invoking next.
In the new design, subsequent Middleware will only execute if the next function is invoked.
