Using Rspack
Rspack is a high performance JavaScript bundler written in Rust. It offers strong compatibility with the webpack ecosystem, allowing for seamless replacement of webpack, and provides lightning fast build speeds.
Compared to webpack, Rspack has significantly improved build performance, thanks not only to the language advantages brought by Rust, but also to its parallel architecture and incremental compilation features. Benchmarking has shown that Rspack can provide 5-10 times better compilation performance.
Modern.js provides out-of-the-box Rspack support, so you can switch between the stable webpack and the faster Rspack.
This document will show you how to enable Rspack build mode in Modern.js.
Initializing an Rspack project
The Modern.js new project has enabled Rspack by default. Just execute Initialize Project to create an Rspack project:
$ npx @modern-js/create@latest myapp
? Please select the programming language: TS
? Please select the package manager: pnpmAfter the project is created, you can experience the project by running pnpm run dev. For more project information, please refer to Quick Start.
Precautions
Before using Rspack, you need to be aware of the following:
- Rspack is compatible with most webpack plugins and almost all loaders, but there are still a few webpack plugins that cannot be used for now. For more details, see Plugin Compatibility.
- Rspack uses SWC by default for code transformation and compression. In rare cases, you may encounter bugs in SWC in edge cases. You can provide feedback via SWC issues.
Migrating configuration
In Modern.js, the tools.rspack and tools.bundlerChain configurations take effect in Rspack mode. If you were previously using webpack mode, after turning on the Rspack build, you can modify it to tools.rspack and tools.bundlerChain.
export default {
tools: {
- webpack: (config, { env }) => {
+ rspack: (config, { env }) => {
if (env === 'development') {
config.devtool = 'cheap-module-eval-source-map';
}
return config;
},
- webpackChain: (chain, { env }) => {
+ bundlerChain: (chain, { env }) => {
if (env === 'development') {
chain.devtool('cheap-module-eval-source-map');
}
},
},
};Modify transpile configuration
Modern.js uses Rspack builtin:swc-loader for code translation in Rspack mode.
Modern.js has provided a more convenient configuration for the common configuration of builtin:swc-loader, such as: configuring the component library to import it on demand through source.transformImport.
If you have custom configuration requirements for builtin:swc-loader, you can set the options of builtin:swc-loader through tools.swc:
import { defineConfig } from '@modern-js/app-tools';
export default defineConfig({
tools: {
swc: {
jsc: {
externalHelpers: false,
},
},
},
});
When Rspack build is enabled, babel-loader is not enabled by default. If you need to add some babel plugins, you can configure it through tools.babel. This will generate additional compilation overhead and slow down the Rspack build speed to a certain extent.
The relationship between Rspack and Modern.js versions
Usually, the latest version of Rspack will be integrated into Modern.js. You can update the Modern.js-related dependencies and built-in Rspack to the latest version by using npx modern upgrade in your project.
However, Modern.js uses a locked version dependency method (non-automatic upgrade) for Rspack. Due to differences in release cycles, the version of Rspack integrated into Modern.js may be behind the latest version of Rspack.
When Rspack is enabled for building through dev / build, the current version of Rspack used in the framework will be printed automatically when debugging mode is turned on:
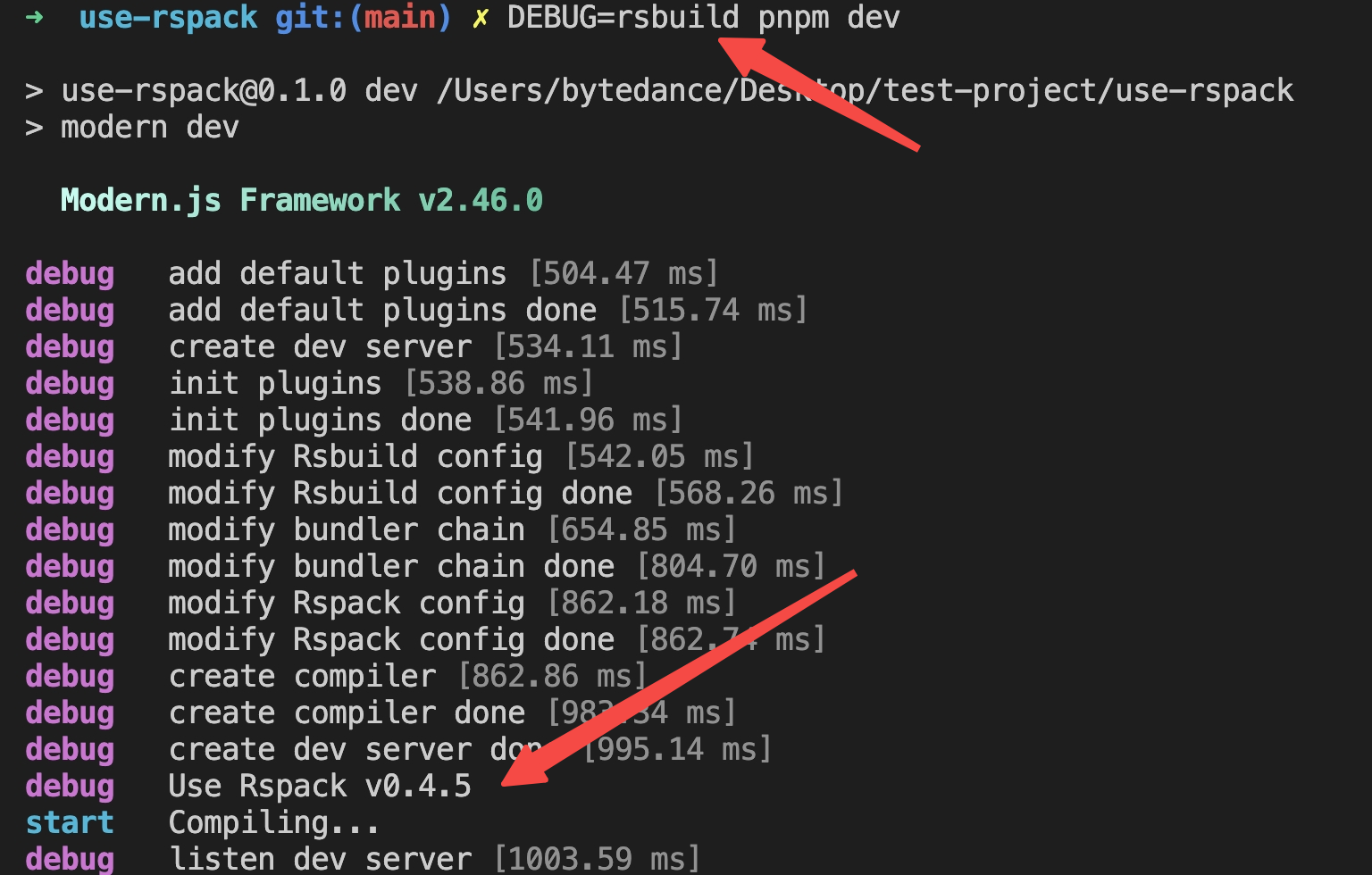
Override the Built-in Rspack Version
You can override Rspack to a specific version using the capbilities provided by package managers such as pnpm, yarn, npm.
For example, if you are using pnpm, you can override the Rspack version with overrides. Assume that the version of Rspack needs to be specified as 0.7.5:
{
"pnpm": {
"overrides": {
"@rspack/binding": "0.7.5",
"@rspack/core": "0.7.5",
"@rspack/plugin-react-refresh": "0.7.5"
}
}
}If you need to use the nightly/canary version of Rspack, the package name of the nightly/canary version of Rspack will be released after adding the -canary suffix, and needs to be modified to:
{
"pnpm": {
"overrides": {
"@rspack/binding": "npm:@rspack/binding-canary@nightly",
"@rspack/core": "npm:@rspack/core-canary@nightly",
"@rspack/plugin-react-refresh": "npm:@rspack/plugin-react-refresh-canary@nightly"
},
"peerDependencyRules": {
"allowAny": ["@rspack/*"]
}
}
}Rspack provides install-rspack tooling to quickly override versions:
npx install-rspack --version nightly # nightly npm tag
npx install-rspack --version 0.7.5-canary-d614005-20240625082730 # A specific canary versionThe Rspack nightly build fully replicates the full release build for catching errors early. Usually it is available and any errors that arise will fixed promptly. However, if there are any break changes that require modern.js to modify the code, we recommend to wait for the next version of modern.js.
More examples of using package managers, please refer to: Lock nested dependency.
